Supervisory team: Marc ZOLGHADRI, Sid-Ali ADDOUCHE
Keywords: Failure diagnosis and prognosis; building upon and leveraging knowledge; supervision; proactive maintenance; availability; Bayesian networks
Research summary
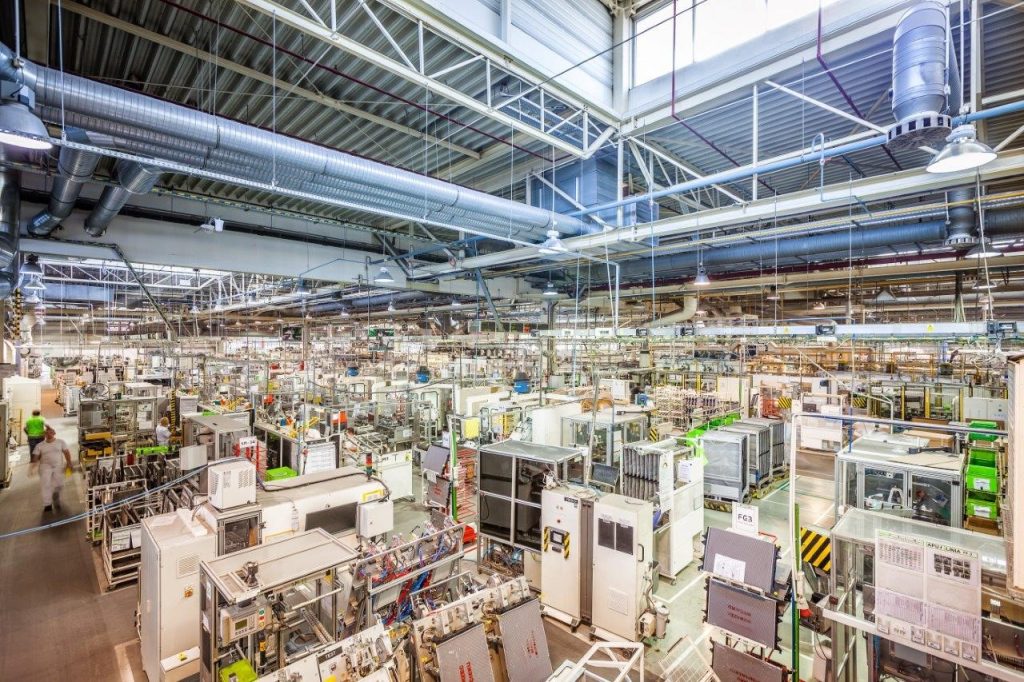
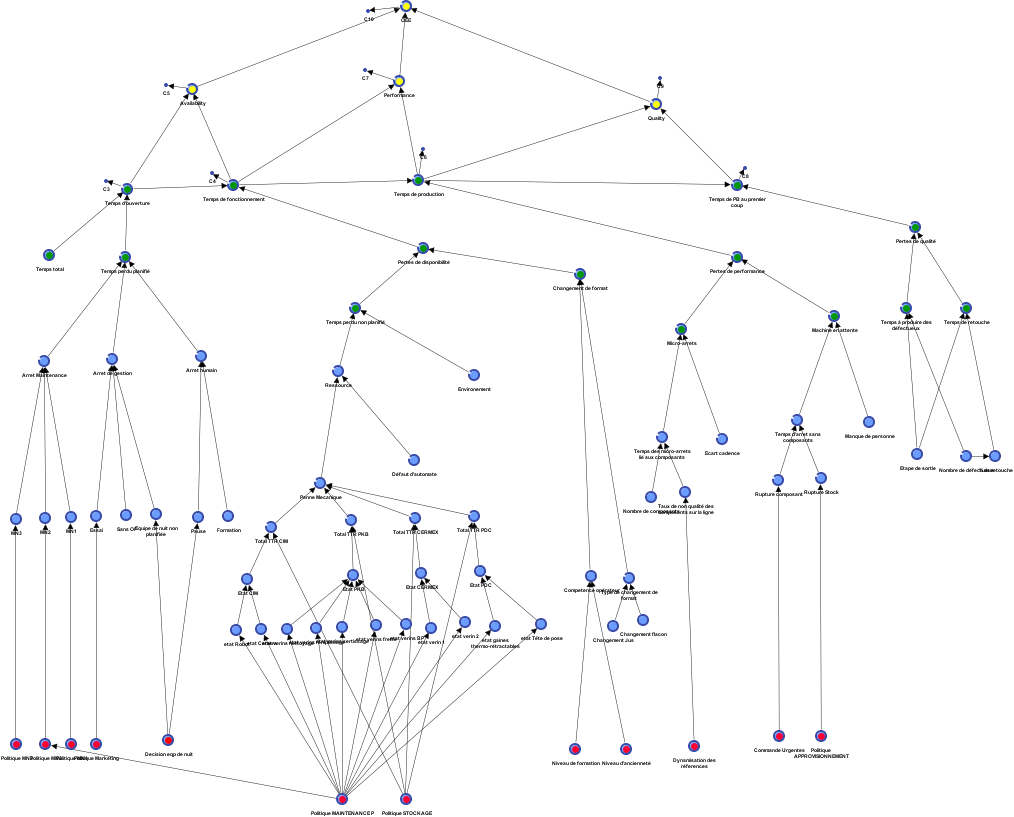
In order to remain competitive, manufacturers in the cosmetics sector must be able to optimise the cost of producing luxury goods. Failure diagnosis and prognosis is an area of interest when improving manufacturing efficiency. The goal of the thesis project is to implement a responsive solution for supervision purposes while ensuring there is a better compromise between equipment availability, operational costs, product quality and competitiveness.
The research explores human expertise as well as a causal-independence reasoning centred on a Bayesian probabilistic formalism, in order to develop a methodology that enables to build a model that estimates production-equipment condition. What stems from the results is a decision-support, overall visualisation tool for manufacturers. This thesis project is conducted in the frame of the French EUGENE project in collaboration with PUIG, PKB and DPS.
Utilising Big Data for Multi-Objective, Performance-Driven Management in the Context of Industry 4.0 – Amel SOUIFI
French supervisory team: Marc Zolghadri, Zohra Cherfi-Boulanger (Professor, University of Technology of Compiègne (UTC))
Tunisian supervisory team: Mohamed Haddar (Professor), Maher Barkallah (Associate professor)
Topic
Generally speaking, production systems must be managed in such a way as to reach their performance objectives. Performance evaluation can include the traditional Time-Cost-Quality triangle but it can also be more complex and involve ecology or human-related aspects.
The advent of Industry 4.0 is putting emphasis on the use of digital twins by businesses for all types of processes. It is very much based on the utilisation of robots. A distinctive aspect of these radical changes occurring in production systems is related to the availability of considerable amounts of data. Another distinctive aspect is related to how these changes will require significant investments before they can generate real benefits. Therefore, industrial management in the digital era requires taking those distinctive aspects into account.
The purpose of this thesis project is to take the concepts related to performance measurement and evaluation and include them into a durable management loop (taking the availability of massive quantities of data into account) for the “hyper-digital” manufacturing industry. The goal is to identify appropriate techniques that enable to:
- evaluate the performance level of actual processes and/or
- estimate performance levels (by anticipation) using digital twins.
Afterwards these measurements/estimates must be used to provide a summary of the best real-time management strategies in the short and medium terms.